In the intricate world of industrial applications, maintaining safety and efficiency is paramount. One of the critical components that plays a pivotal role in ensuring operational integrity is the safety valve. Designed to prevent excessive pressure build-up in systems, safety valves act as the last line of defense against catastrophic failures, protecting both equipment and personnel. This guide will explore the top ten safety valves that you need to know, highlighting their features, applications, and advantages.
Understanding the various types of safety valves available in the market is essential for any industrial operation. From spring-loaded to pilot-operated designs, each safety valve serves a unique purpose tailored to specific conditions and environments. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of these essential devices, providing insights into how to select the best safety valve for your application. Whether you are involved in manufacturing, chemical processing, or oil and gas industries, knowing the right safety valve can significantly influence operational safety and reliability. Join us as we navigate this vital topic, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions for your industrial needs.
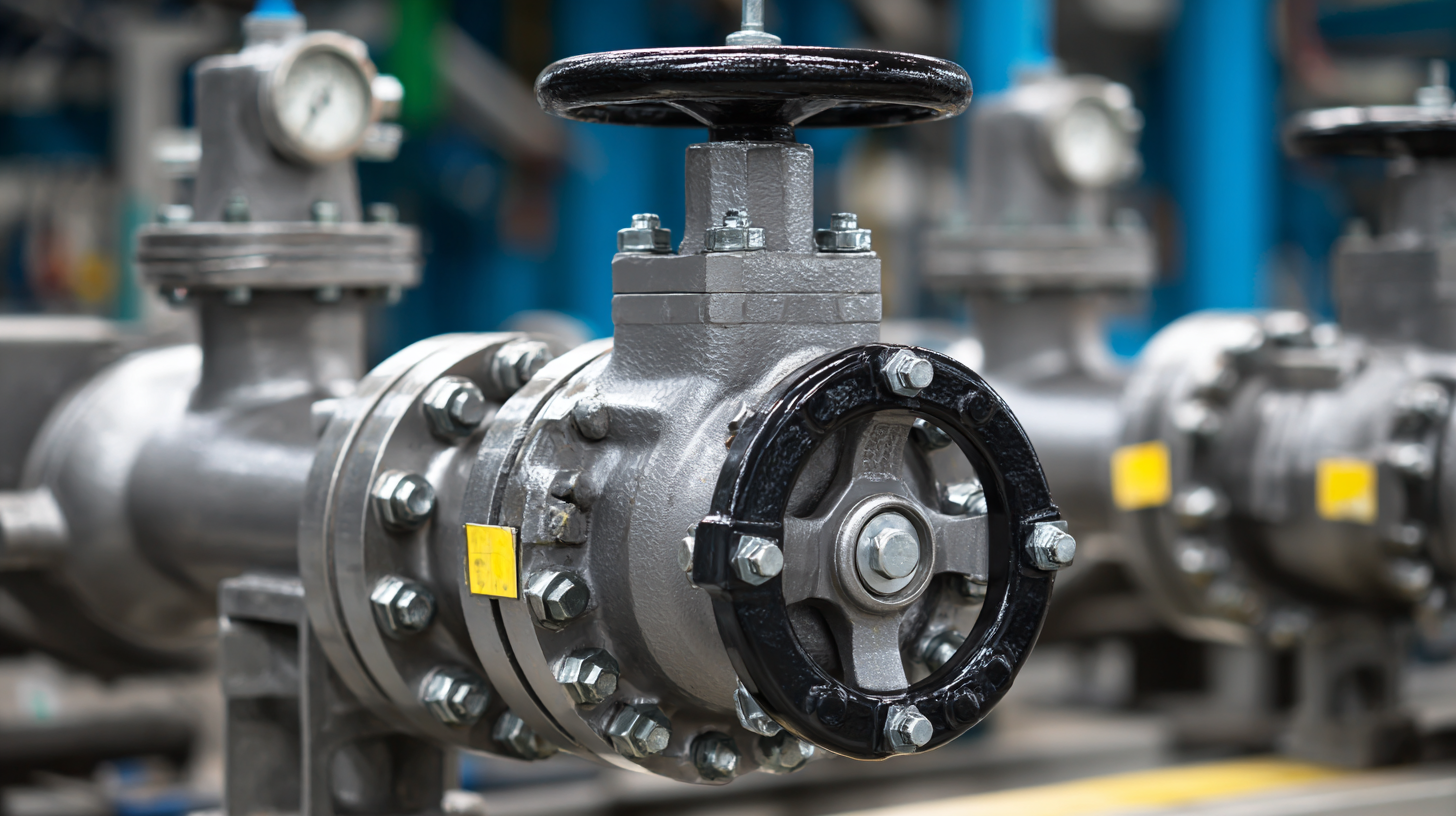

In high-pressure systems, safety valves play a crucial role in ensuring operational safety and equipment protection. Various types of safety valves are utilized across industrial applications, each designed to handle specific pressure requirements and media types. Among the most common are spring-loaded safety valves, which are widely favored for their simplicity and reliability. These valves use a spring mechanism to maintain a predetermined pressure, automatically opening to release excess pressure and preventing equipment failure.
Another significant type is the pilot-operated safety valve, which utilizes a smaller pilot valve to control the opening of the main valve. This design provides enhanced precision and responsiveness to pressure fluctuations, making it ideal for high-pressure steam systems. Additionally, rupture disks are often used in conjunction with safety valves for ultimate pressure relief, offering a fail-safe solution that quickly vents excess pressure without the need for mechanical operation. Understanding these types of safety valves and their applications is essential for maintaining safety standards in any industrial high-pressure environment.
When selecting safety valves for industrial applications, understanding the common materials and designs is crucial for ensuring performance and reliability. Safety valves are typically constructed from high-quality materials that can withstand extreme pressures and temperatures. Stainless steel is one of the most popular materials due to its excellent corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for various environments, including chemical processing and oil and gas sectors. Other materials such as brass, cast iron, and high-performance plastics are also used, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
In terms of design, safety valves come in several types, each suited for different operating conditions. The most common designs include spring-loaded and pilot-operated valves. Spring-loaded safety valves are often preferred for their simplicity and quick response times, while pilot-operated valves are favored in applications requiring precise pressure control and stability under variable conditions. Understanding these materials and designs helps engineers and operators select the right safety valve, ensuring that they effectively protect equipment and personnel while complying with safety regulations.
Safety valves play a crucial role in protecting industrial systems from overpressure, and understanding the differences between spring-loaded and pilot-operated types is key for selecting the right solution. Spring-loaded safety valves rely on a spring mechanism to maintain balance against system pressure, naturally allowing for quicker response times under normal conditions. According to a report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), approximately 70% of the safety valves utilized in various industries are of the spring-loaded variety due to their simplicity and reliability in straightforward applications.
In contrast, pilot-operated safety valves utilize a pilot system to manage flow, providing a greater degree of precision and efficiency. This type is often preferred in high-pressure applications as they can handle larger volumes with lower set pressure variations—making them ideal for complex systems. Industry data indicates that using pilot-operated valves can reduce emissions by as much as 30%, underscoring their value in both safety and environmental compliance.
**Tip:** When choosing a safety valve, consider not only the specific application but also the system’s pressure characteristics. Always consult with safety valve manufacturers for tailored recommendations to ensure optimal performance.
**Tip:** Regular maintenance and testing of safety valves are essential. Conduct routine checks on both spring-loaded and pilot-operated valves to ensure they function correctly and meet industry standards.
| Valve Type | Operating Mechanism | Typical Applications | Set Pressure Range (psi) | Material | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring-Loaded | Mechanical - Spring | Boilers, Pressure Vessels | 15 - 3000 | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel | Quick Response, Simplicity |
| Pilot-Operated | Pneumatic Control | Gas Storage, Process Systems | 50 - 6000 | Aluminum, Alloy Steel | High Capacity, Stable Operation |
| Direct-Relaxation | Spring Mechanism | Oil and Gas Industries | 30 - 4000 | Bronze, Stainless Steel | Compact Design, Economic |
| Balanced Bellows | Spring with Bellows | Power Plants, Refineries | 100 - 3000 | Stainless Steel, High Alloy | Reduced Chattering, Performance Stability |
| Sanitary | Spring Mechanism | Pharmaceuticals, Food Processing | 15 - 300 | Stainless Steel | Hygienic Design, Easy Cleaning |
| Valve with Fail-Safe | Pilot Operated | Chemical Processing | 50 - 5000 | Special Alloys | Safety Assurance, Consistent Performance |
| High-Pressure | Spring-Loaded | Hydraulic Systems | 100 - 10000 | Carbon Steel | Durable, High Flow Rate |
| Low-Pressure | Pilot Operated | Wastewater Treatment | 10 - 150 | PVC, Polypropylene | Corrosion Resistant, Lightweight |
| Expanding Seat | Mechanically Actuated | Pipelines, Mining | 150 - 6000 | Steel, Brass | Stable Seating, Prevention of Leakage |
When selecting the right safety valve for industrial applications, there are several key factors to consider. The valve's material compatibility is essential, especially in industries dealing with corrosive substances or extreme temperatures. For example, the growing demand for acidic gas valves, projected to reach $14.709 million by 2032 with a 5.1% CAGR, highlights the importance of selecting valves that can withstand corrosive environments. Additionally, the application’s pressure and temperature specifications must match the safety valve’s rating to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Another critical factor is the valve's size and flow characteristics, which directly impact the process efficiency. In the pharmaceutical industry, diaphragm valves are increasingly gaining traction, with the market expected to grow from $123.3 million in 2024 to $284.6 million by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 11.02%. This underscores the necessity of choosing the right valve type based on the specific requirements of the application, ensuring that safety and regulatory standards are met.
Tips: Always consult industry standard guidelines and seek expertise when selecting safety valves to enhance operational safety. Consider conducting thorough market research to stay informed about emerging technologies and trends relevant to your specific industry needs. Make use of performance data and expert recommendations to optimize your valve choice.
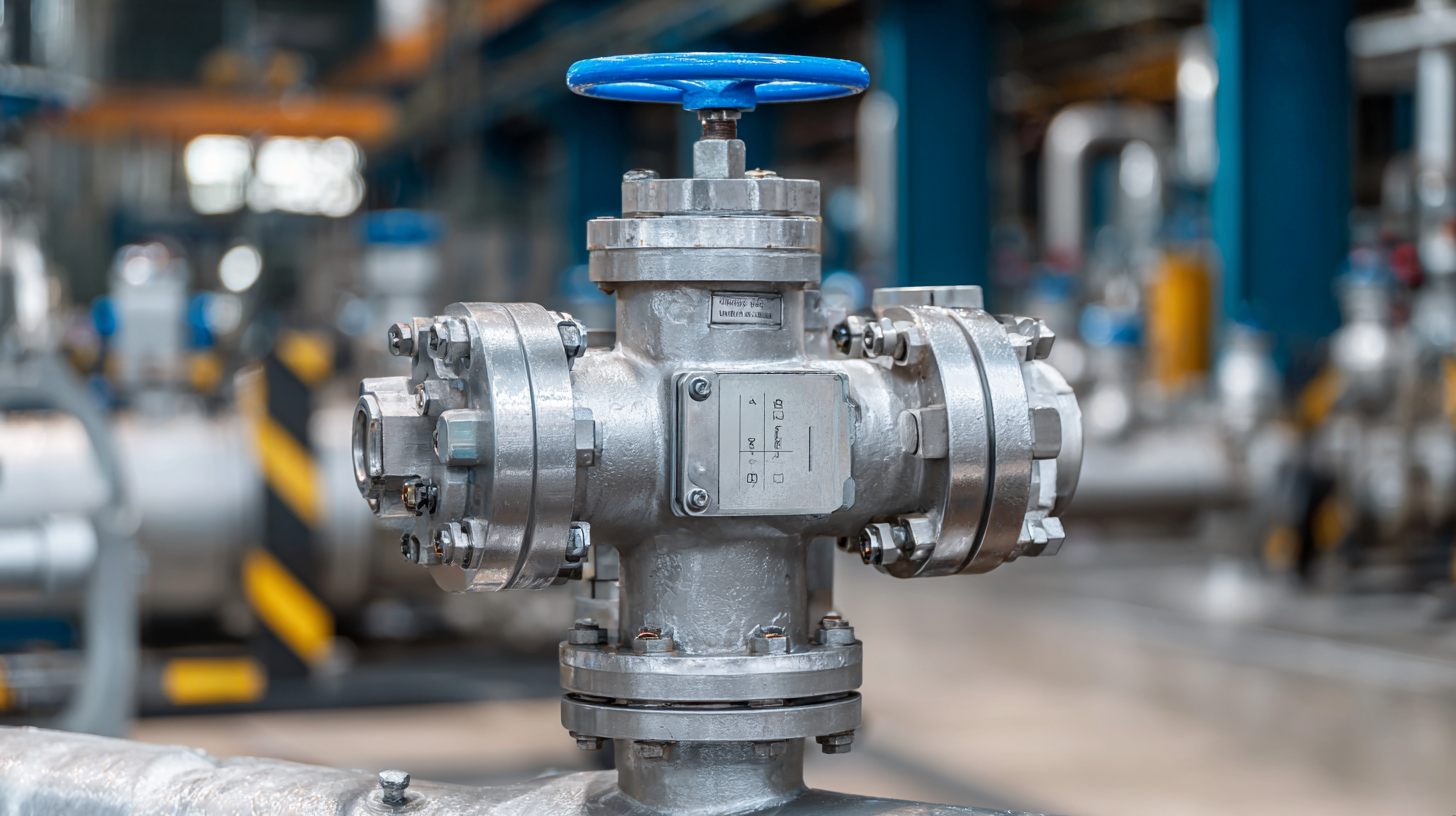

Ensuring the functionality of safety valves is paramount in industrial applications to prevent catastrophic failures. According to a report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), nearly 60% of industrial accidents can be attributed to faulty safety devices, highlighting the importance of regular maintenance. A thorough maintenance program can significantly reduce the risk of malfunctions and extend the lifespan of safety valves. Regular testing and inspections can identify potential issues before they lead to operational failures.
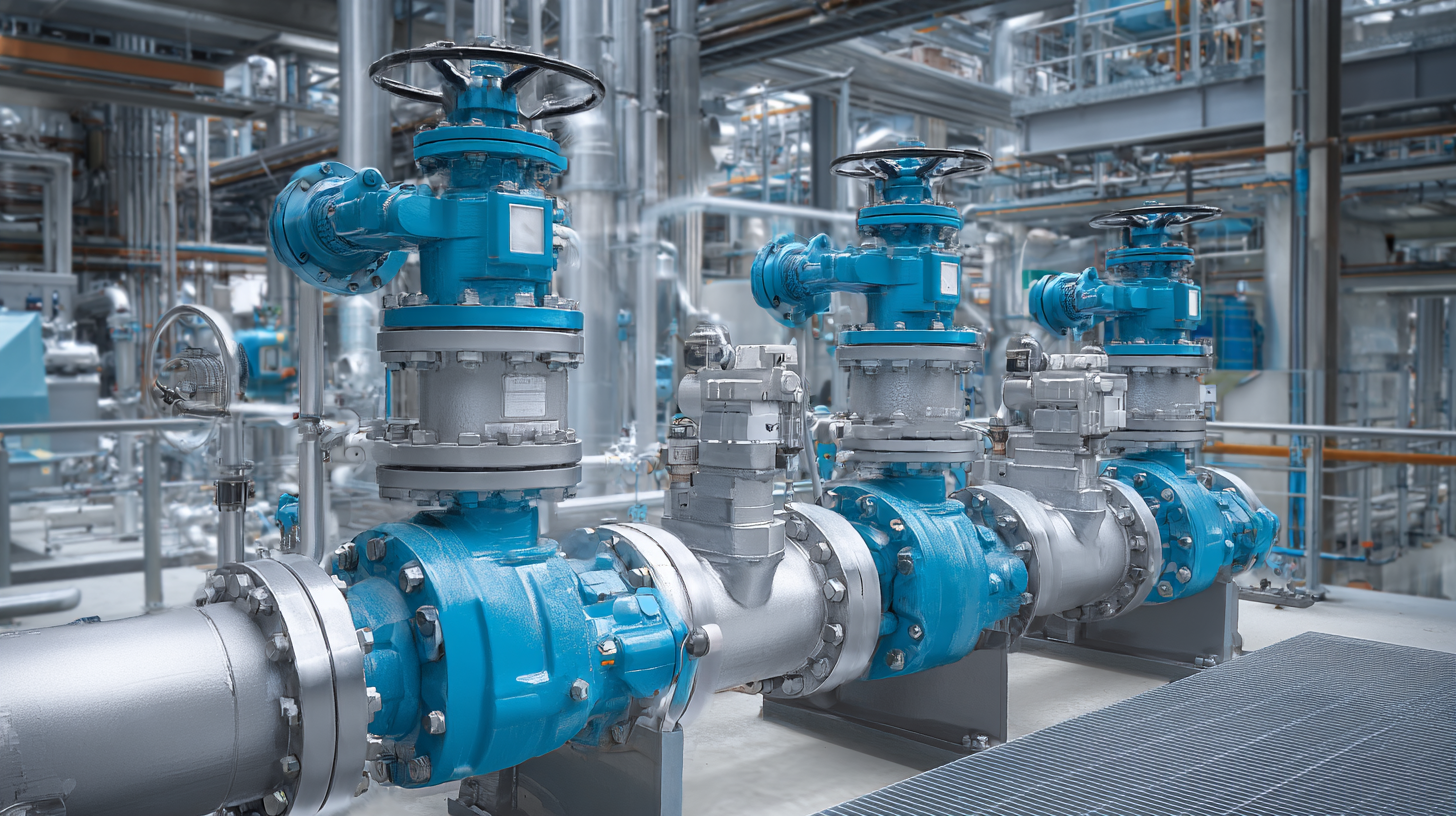

Tips for maintenance include conducting routine visual inspections to spot any signs of corrosion or wear. Additionally, calibrating safety valves at regular intervals is essential to ensure they open and close at the specified pressures. According to the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors, calibration should be performed at least annually to adapt to any changes in system conditions.
Another critical practice is to document all maintenance activities meticulously. This documentation helps track the performance of safety valves over time and facilitates compliance with safety regulations. A survey by the International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam (IAPWS) emphasizes that having an effective maintenance log can reduce downtime by up to 30%, proving the importance of proactive management in maintaining safety equipment.






© Shipham Valves 2025. All Rights Reserved.
Website By PS Website Design Ltd
Request a Quote/Further Information
Download
We use cookies on this website, by continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Find out more.